Chemistry
I would like to take this opportunity to welcome pupils past, present and future, and parents to the Chemistry department within Banbridge Academy.
STAFF:
Head of Department Mrs J Glover
Members of the Department Mrs H Morrison, Dr C Lorimer, Mr C Beacom, Mrs R Thompson, Mrs B Kernaghan
Chemistry is concerned with the building blocks of all materials – the elements.
We are interested in the properties of these elements, how they react together, and the properties of the compounds that are formed.
Today’s Chemists are involved in researching the fight against disease by creating and modifying molecules to produce new and useful materials such as pharmaceuticals. They are helping to feed the world in the understanding of processes involved in the production of fertilisers so we can provide enough food to feed billions of people on a future Earth. Chemistry has a key role to play in meeting the global challenge of making cities safe, resilient and sustainable as nearly 70% of the world population lives in urban areas and climate change is a topic on everyone’s mind, Chemistry students will be learning about carbon dioxide, solutions, pH and acid/base reactions will be interested and worried when that knowledge is placed in the context of ocean acidification and damage to marine ecosystems.
Our overall aims are:-
- stimulate an enjoyable interest in the subject;
- provide a body of knowledge relevant to both those who intend to continue with the study of Chemistry and to those who do not;
- promote an understanding of chemical patterns and principles;
- develop an appreciation of both the benefits and potential hazards of chemicals and their use;
- encourage the application of knowledge and understanding to unfamiliar situations;
- develop abilities of interpretation, organisation and evaluation of data together with its communication;
- teach positive cooperation with others through group experimental work;
- develop an appreciation of the scientific, social, economic, environmental and technological contribution of chemistry and its applications;
- give some appreciation to the historical significance of chemistry in world development.
FACILITIES
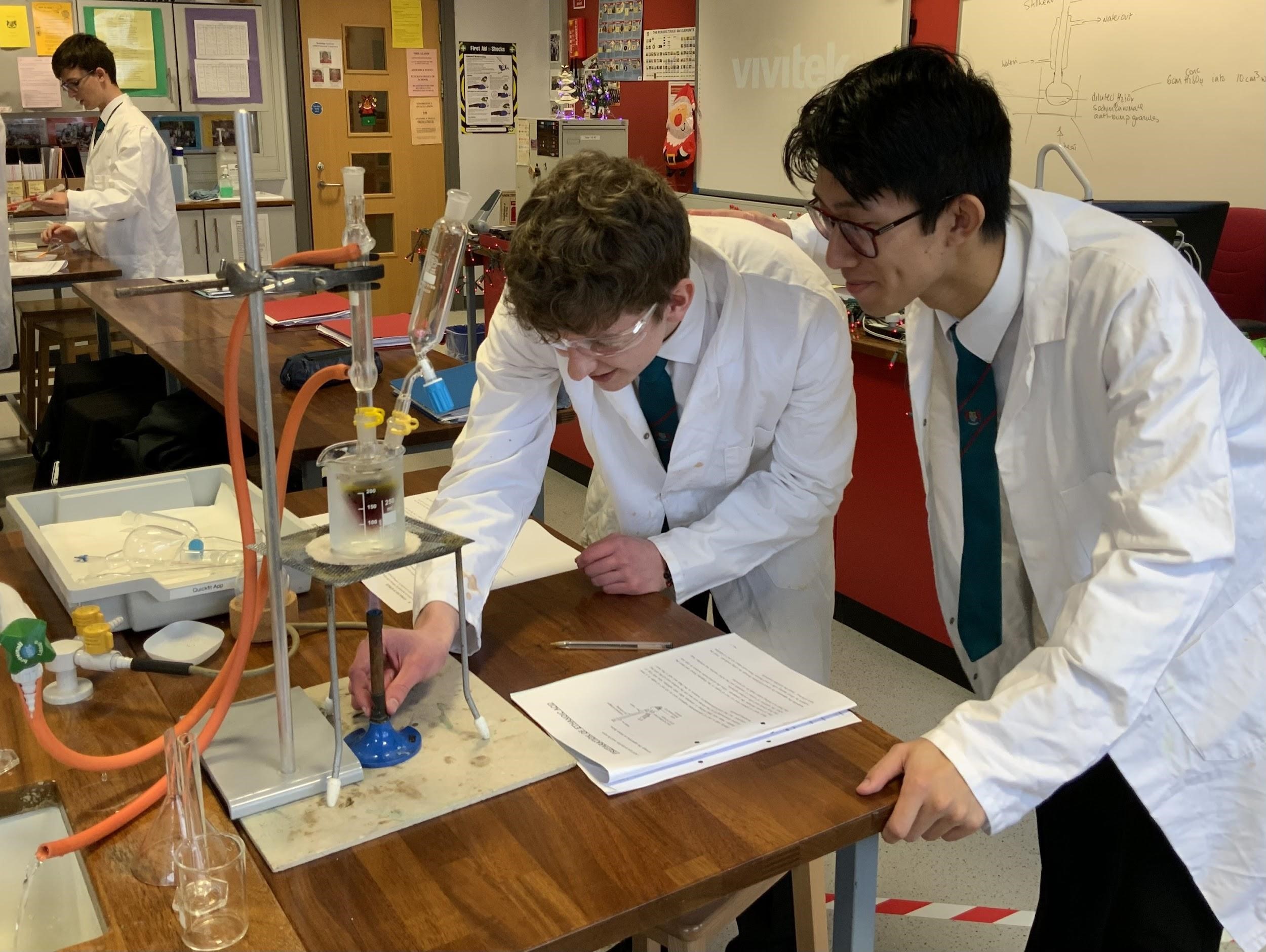
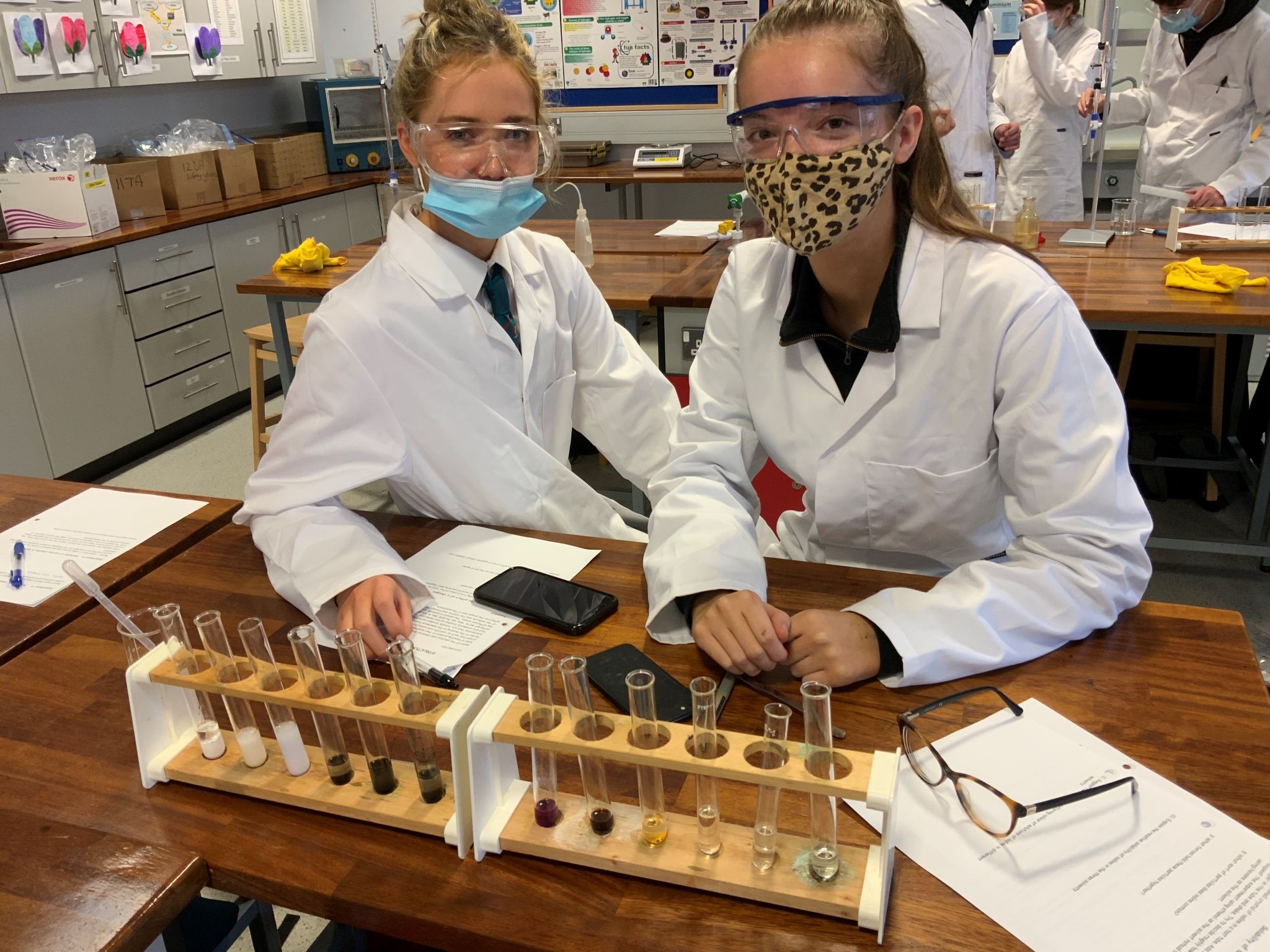
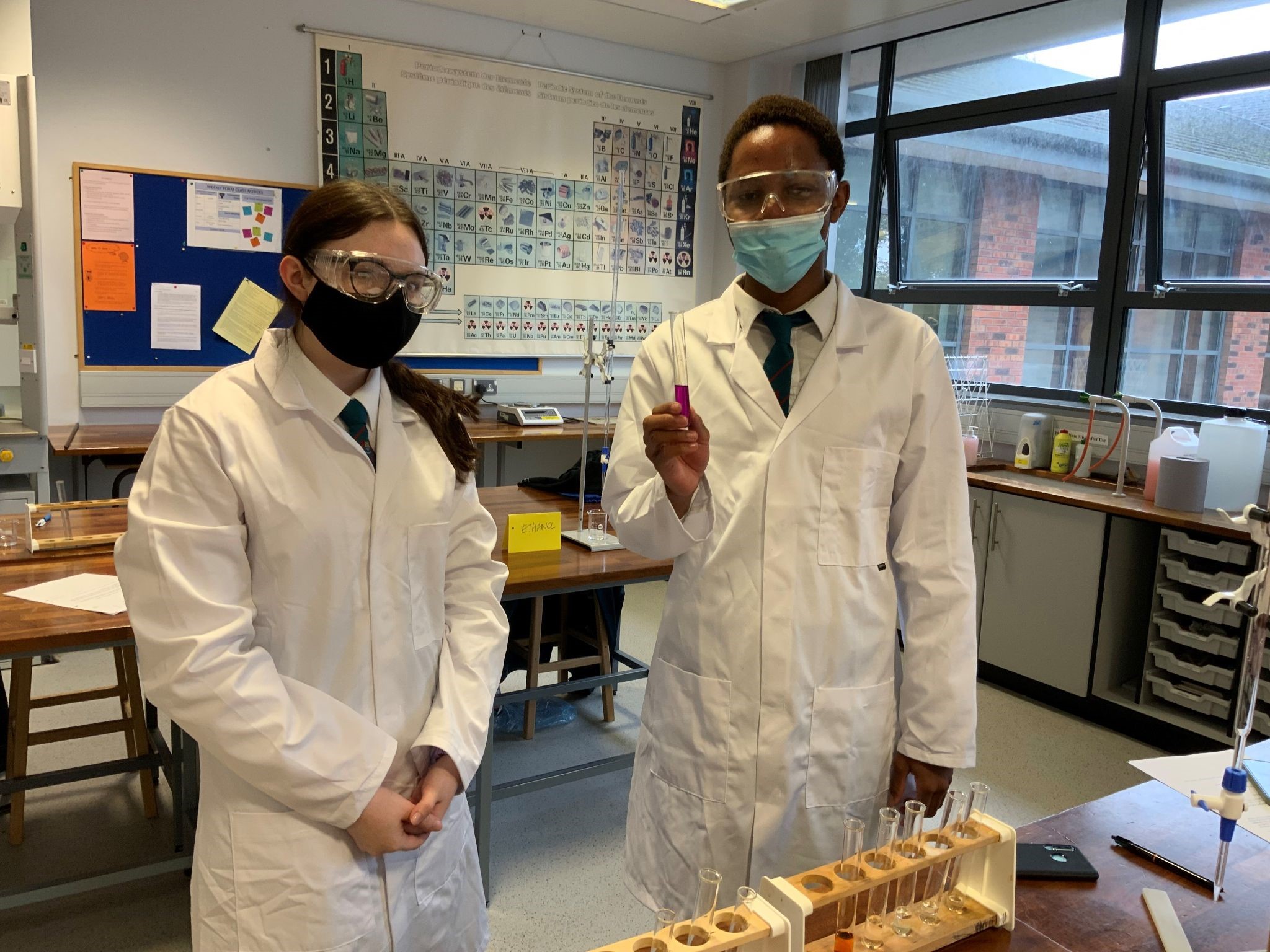
Chemistry is taught in 5 specialist laboratories. These provide excellent facilities and offer wide opportunities for both teaching and experimental work.
KEY STAGE 3
In Years 8 & 9 the Chemistry Department contributes into the teaching of a combined Science course. Then in Year 10 it is taught as a discrete subject by specialist Chemistry teachers. Topics covered include:-
| Year 8 | Year 9 | Year 10 |
| Practical Skills
Kinetic Theory Separating Techniques |
Atoms, Elements, Compounds & Mixtures
Acids & Alkalis Solubility Air |
Atomic Structure
Ionic Bonding Balancing Equations Acids, Bases & Salts Periodic Table Preparation of Gases |
GCSE CHEMISTRY
Pupils will be entered for the GCSE Chemistry specification offered by CCEA at the Higher Tier Level. This course helps prepare pupils for the study of Chemistry and related subjects at a more advanced level. A GCSE in Chemistry is relevant not only to the field of science but also to areas of commerce and public service that value problem-solving and practical skills.
As well as being an interesting and enjoyable subject, it is also an important and often essential subject choice for many career paths including medicine, dentistry, veterinary medicine and the biomedical sciences.
The Practical Skills Unit makes up 25% of the qualification. The acquisition and development of the skills needed for this unit will form part of the normal classroom teaching and learning. A series of prescribed practical tasks will be carried out as part of the course. Students will be assessed in practical skills in the second term in Year 12 and will also answer structured questions set in a practical context in a written practical exam.
TRIPLE AWARD Course Content – 3 externally examined Units
Unit 1: Structures, Trends, Chemical Reactions, Quantitative Chemistry and Analysis
Unit 2: Further Chemical Reactions, Rates and Equilibrium, Calculations and Organic Chemistry
Unit 3: Practical Skills
DOUBLE AWARD Course Content – 3 externally examined Units
Unit 1: Structures, Trends, Chemical Reactions, Quantitative Chemistry and Analysis
Unit 2: Further Chemical Reactions, Rates and Equilibrium, Calculations and Organic Chemistry
Unit 3: Practical Skills
Currently Double Award candidates are given the opportunity to sit their external Unit 1 examination in November of Year 12 with the remaining units in the following summer.
GCE CHEMISTRY
The Chemistry Department seeks both to teach the essential principles of Chemistry and to equip pupils with relevant experimental skills. Every year quite a large number of pupils go on to study Chemistry at AS or A level either with a view to pursuing a scientific career, as a necessary step to university courses such as Medicine, Dentistry, Chemical Engineering and Pharmacy, or simply because they enjoy the subject.
Course Content:
3 externally marked AS modules are studied in Year 13 and the examinations taken in the summer of that year. 3 externally marked A2 modules are covered in Year 14 and the examinations again taken in the summer.
AS 1: Basic Concepts in Physical and Inorganic Chemistry
AS 2: Further Physical and Inorganic Chemistry and an introduction to Organic Chemistry
AS 3: Basic Practical Chemistry
A2 1: Further Physical and Organic Chemistry
A2 2: Analytical, Transition Metals, Electrochemistry and Organic Nitrogen Chemistry
A2 3: Further Practical Chemistry
CAREERS IN CHEMISTRY
Commerce – The commercial sector is one of the largest employers of chemistry graduates after the chemical industry. Employers recognise the key skills of numeracy, problem solving and communication that are an integral part of all chemistry degrees.
Teaching – Teachers enjoy challenges and rewards that few other jobs can offer. These include variety and constant intellectual stimulation.
Science Journalism – Science journalists have a role to play in acting as intermediaries between science and the public. Journalists work in all areas of the media: television, radio, newspapers or specialist science magazines.
Careers in Law – Patent agents are professionals who have grounding in science and are trained in specialist areas of law.